Describe Passive Transport Across a Biological Membrane
The one essential requirement for passive transport is that a concentration gradient must exist between one side of the membrane and the other. Briefly describe the two types of passive transport across membranes.
(36).jpg)
Transport Across The Cell Membrane Trivia Quiz Proprofs Quiz
It allows some things to pass through but stops others.
(36).jpg)
. A membrane is a selective barrier. It regulates what enters and exits the cell and organelles. Membrane proteins serve several functions including cell-to-cell communication and interaction molecular transport and cell signaling.
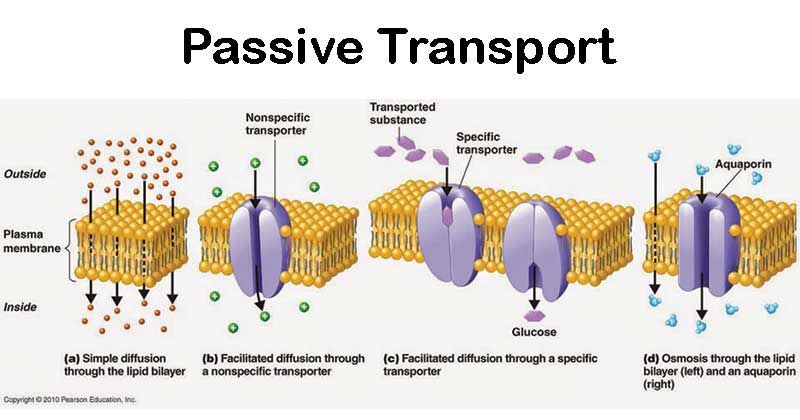
Not surprisingly the aquaporin proteins that facilitate water movement play a large role in osmosis most prominently in red blood cells and the membranes of kidney tubules. Describe the direction of the movement of the molecules in Model 1. Osmosis is a passive transport system meaning it requires no energy.
Such things may be molecules ions or other small particlesMembranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Transport across cell membrane is classified into four ways. The dots because they are small and can fit though the gaps and because they are shown as equally distributed on both sides of the membrane.
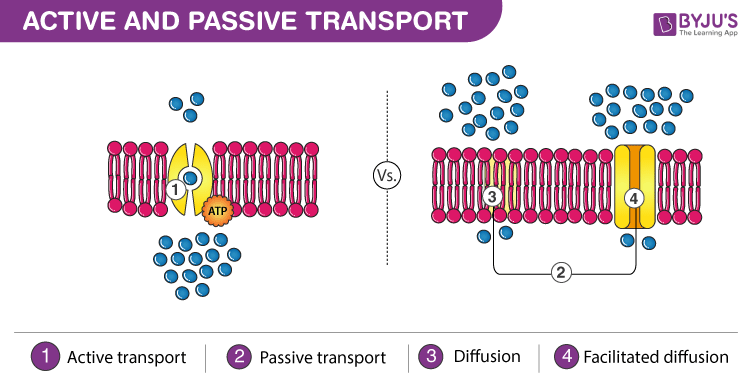
Passive transport does not require energy in the form of ATP. Active transport allows cells to reside in a constant state of non-equilibrium. The fluid mosaic model also helps to explain.
Model 2 The Selectively Permeable Cell. To understand passive processes you must first accept and understand that molecules are constantly in motionThe random movement of solutes in solution resulting from the bombardment of water molecules. As seen in the previous sections they form complex arrays hierarchical structures and are often multifunctional ie one material has more than one function.
Which molecules are able to pass through the semi-permeable membrane. In a process scientists call phagocytosis other cells can engulf large particles such as macromolecules cell parts or whole cells. The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds each cell and some organelles.
This movement is caused by a concentration gradient created when there are different solute concentrations inside and outside the cell. Briefly describe active transport across the membranes 9. Across biological membrane is dependent on specific.
Biological materials are more complex than synthetic materials. Biological membranes include cell membranes outer coverings of cells or organelles that allow passage of certain constituents. Neurons and Glial Cells.
Describe the structure and function of neuronal synapses and the role of neurotransmitters at the synapse. Passive transport relies on the natural kinetic energy and random movement of molecules. Special membrane proteins can cotransport two solutes by coupling diffusion down a concentration gradient to transport against the concentration gradient.
Cell membrane cell wall chloroplasts lysosome Golgi endoplasmic reticulum vacuoles ribosomes and mitochondria interact as a system to maintain homeostasis. Cell membrane acts as a barrier to most but not all molecules. We classify biological materials from the mechanical property viewpoint into soft and hard.
Hard materials provide the. List the common features of the models of membran transport systems 38. Transport Across The Membrane Anatomy Of The Cell Cell and Cell Theory Home Cell Organelles and Their Functions Cell Organelles and Their Functions 2006 10 October 10 Example Pages and Menu Links I installed with my own language but the Back-end is still in English.
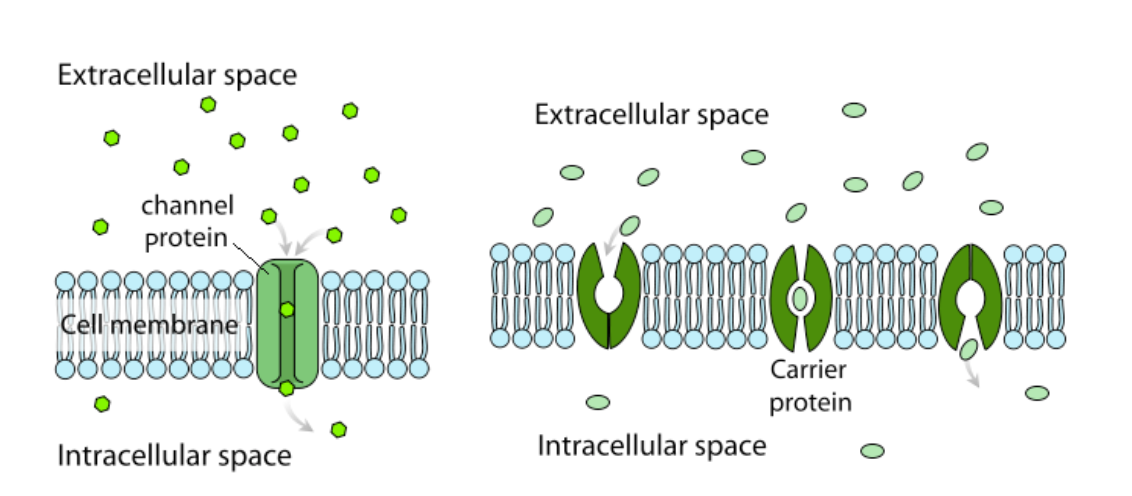
It causes water to move in and out of cells depending on the solute concentration of the surrounding environment. Symptoms of a COPD include shortness of breath a chronic or persistent cough chest tightness wheezing and difficulty breathing when exercising or during any physical activity. These proteins act like gates to allow large molecules like glucose to get across the membrane.
The fluid mosaic model of the membrane was first outlined in 1972 and it explains how biological molecules are arranged to form cell membranes. Learning Outcomes By the time you are done with this. While diffusion transports materials across membranes and within cells osmosis transports only water across a membrane.
Active transport methods require directly using ATP to fuel the transport. Draw the general structure of Phospholipid 10. Develop and use models to explain the role of cellular reproduction including binary fission mitosis and meiosis in maintaining genetic continuity.
The semipermeable membrane limits the diffusion of solutes in the water. This condition powers advanced functionalities such as motility 10 sensing 11 and autonomous self-replication 1213. Diffusion Passive Transport 2.
Construct arguments supported by evidence to relate the. Phospholipids structurally contain two distinct regions. If glucose tried to cross the membrane without the protein gate it would take a.
Cell membranes are semi-permeable barrier separating the inner cellular environment from the outer cellular environment. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD includes a range of lung-based diseases such as asthma chronic bronchitis and emphysema. In phagocytosis a portion of the membrane invaginates and flows around the particle eventually pinching off and leaving the particle entirely enclosed by a plasma.
Since the cell membrane is made up of a lipid. Transport Across The Membrane Anatomy Of The Cell Cell and Cell Theory Home Cell Organelles and Their Functions Cell Organelles and Their Functions 2006 10 October 10 Example Pages and Menu Links I installed with my own language but the Back-end is still in English. Passive and active movement between cells and their surroundings.
When the proteins of the pump are first synthesized in the rough ER what side of the ER membrane. The sodium-potassium pump in animal cells requires cytoplasmic ATP to pump ions across the plasma membrane. The information below was adapted from OpenStax Biology 351 and Khan Academy AP Biology The neuron and nervous system.
The nervous system is made up of neurons the. It doesnt matter what dissolved. Transport Across Cell Membrane - Key takeaways.
No comments for "Describe Passive Transport Across a Biological Membrane"
Post a Comment